Experiences from SAP internal Validation Project
My colleague Eduard Stelle and I are recently worked in an SAP internal validation project where we tested the conversion from SAP ERP to S/4HANA including an integration to SAP Cloud for Customer. This blog describes our proceeding and experiences with focus on the SAP Clod for Customer relevant activities.

Links
This Blog post as PDF file:
https://www.sap.com/documents/2018/09/925c68a9-1d7d-0010-87a3-c30de2ffd8ff.html
openSAP course on System Conversion to SAP S/4HANA:
https://open.sap.com/courses/s4h11
Blog on alternate mashup integration approached to substitute ERP Cockpit with S/4HANA Fiori App:
https://blogs.sap.com/2018/02/15/cloud-for-customer-mashup-call-an-erp-transaction-in-sap-gui-for-ht…
SAP S/4HANA Cookbook – Customer/Vendor Integration (further updates planned):
https://support.sap.com/content/dam/SAAP/SAP_Activate/S4H.0781%20SAP%20S4HANA%20Cookbook%20Customer%…
Conversion Guide for SAP S/4HANA 1610:
https://help.sap.com/http.svc/rc/PRODUCTION/pdfe68bfa55e988410ee10000000a441470/1610%20000/en-US/CON…
Overview : Conversion Project Goal & Scope
The conversion activities were part of an SAP internal project with the following goals:
-
- Conversion of a C4C integrated SAP ERP system to S/4HANA
-
- Technical and functional checks with focus on the C4C integration during and after the conversion
-
- Verify the Integration quality and robustness
-
- Create a reference task list and process description
-
- Verify the Integration quality and robustness
This document is meant to provide an overview and the details of the conversion activities we have performed with regards to the C4C integration in the SAP internal project. Our approach and experiences can be used as a baseline to assess and to plan customer specific conversion projects were C4C integration is involved. However, the actual steps in a customer projects are heavily depending on the customer specific situation and require final and individual assessment.
The project was carried out in 1H/2018 by the integration experts of the C4C Expert Service Team: Eduard Stelle, Bernd Fleddermann, Carolin Hormuth
Disclaimer
The conversion project was carried out on an SAP internal test landscape with a predefined functional and integration scope
-
- The required steps and processes in a customer specific environment may vary from the described processes and requires dedicated and individual planning and test
-
- Future developments might impact the conversion activities as described
-
- This document focuses on the SAP Cloud for Customer integration and their relevant activities. The setup on the SAP ERP, S/4HANA side requires also extensive activities described in dedicated guidelines:Selection of S/4Hana conversion guidelines:
-
- SAP S/4HANA Cookbook – Customer/Vendor Integration
(https://support.sap.com/content/dam/SAAP/SAP_Activate/S4H.0781%20SAP%20S4HANA%20Cookbook%20Customer%…)
- SAP S/4HANA Cookbook – Customer/Vendor Integration
-
- Conversion Guide for SAP S/4HANA 1610
(https://help.sap.com/http.svc/rc/PRODUCTION/pdfe68bfa55e988410ee10000000a441470/1610%20000/en-US/CON…)
- Conversion Guide for SAP S/4HANA 1610
-
- openSAP course on System Conversion to SAP S/4HANA
-
- This document focuses on the SAP Cloud for Customer integration and their relevant activities. The setup on the SAP ERP, S/4HANA side requires also extensive activities described in dedicated guidelines:Selection of S/4Hana conversion guidelines:
To plan and perform the conversion activities in a productive customer environment it is recommended to get support from SAP ERP-, S/4HANA (conversion) experts and SAP Cloud for Customer expert service.
Initial Replication Scenarios
We have decided on the integration scenarios as listed below. The selection is meant as a representative subset of the entire integration scope covering typical use cases:
-
- Bi-directional Account Replication and other master data
-
- Replication of transactional documents including (bi-directional replication)
-
- IDoc based integration with asynchronous processing
-
- synchronous web services
-
- Extension scenarios
-
- Typical configuration (for example: standard prospect blocking in C4C; Filter settings)

Figure 1: 01_01_MasterDataView
Material Replication from SAP Business Suite
Inbound Services C4C:
-
- Replicate Material from SAP Business Suite
-
- Replicate Material Attachment from SAP Business Suite
Outbound Services C4C:
-
- Confirm Material Replication to SAP Business Suite
Business Partner Replication from SAP ERP
Inbound Services C4C:
-
- Replicate Business Partner from SAP ERP
-
- Replicate Business Partner Address from SAP ERP
-
- Replicate Business Partner Contact Address from SAP ERP
Additional Configuration:
-
- Prospect Update Scenario – “Prospect in Cloud, create customer in SAP ERP manually and link back convert Cloud prospect to account”.
The implementation of this scenario in SAP ERP is described in the C4C blog post “Create prospect in Cloud for Customer and convert to account through ERP customer creation“
(https://blogs.sap.com/2018/04/24/create-prospect-in-cloud-for-customer-and-convert-to-account-through-erp-customer-creation/)
- Prospect Update Scenario – “Prospect in Cloud, create customer in SAP ERP manually and link back convert Cloud prospect to account”.
-
- Segment Filter SAP ERP Outbound
A segment filter was implemented in SAP ERP (Transaction BD64) to filter out Sales Data of a specific Sales Organization in the SAP ERP outbound IDocs
- Segment Filter SAP ERP Outbound
-
- Filter BAdI SAP ERP Outbound
-
- The BAdI IDOC_CREATION_CHECK was implemented to prevent the SAP ERP outbound replication of certain Business Partners
-
- Customer Extension
-
- A custom field was added to the DEBMAS IDoc, which was mapped to a custom field in C4C. The procedure of the extension scenario is described in the C4C blog post “Cloud for Customer Integration with SAP ERP – replicate a custom own field in the customer master t…
(https://blogs.sap.com/2018/04/24/cloud-for-customer-integration-with-erp-replicate-a-custom-own-field-in-the-customer-master-through-idoc-extension/)
- A custom field was added to the DEBMAS IDoc, which was mapped to a custom field in C4C. The procedure of the extension scenario is described in the C4C blog post “Cloud for Customer Integration with SAP ERP – replicate a custom own field in the customer master t…
Business Partner Replication to SAP ERP
Outbound Services C4C:
-
-
-
- Replicate Business Partner to SAP ERP
-
- Replicate Business Partner Address to SAP ERP
-
- Replicate Business Partner Contact Address to SAP ERP
-
-
Additional Configuration:
-
- Standard prospect Filter C4C Outbound (C4C Business Configuration Question à Communication and Information Exchange à Integration with External Applications and Solutions à Integration with SAP ERP à “Do you want to block prospects created in Cloud Solution from being replicated to your SAP ERP solution?”
-
- The Enhancement Option “CheckBusinessObjectInstanceProcessIntegrationRelevance” was implemented to prevent the C4C outbound replication of certain Business Partners

Figure 2: 01_02 Transaction View
Contract Replication from and to SAP Business Suite
Inbound Services C4C:
-
- Replicate Contract from SAP Business Suite
-
- Replicate Contract Attachment from SAP Business Suite
Outbound Services C4C:
-
- Replicate Contract to SAP Business Suite
-
- Confirm Contract Replication to SAP Business Suite
-
- Replicate Contract Attachment to SAP Business Suite
Pricing in Contract Replication Scenario in SAP Business Suite
Outbound Services C4C:
-
- Request Contract Data from SAP Business Suite
Creation of Opportunity Follow Up Document in SAP Business Suite
Inbound Services C4C:
-
- Notify Opportunity of Follow Up Document from SAP Business Suite
Outbound Services C4C:
-
- Create Opportunity Follow Up Document in SAP Business Suite
-
- Replicate Opportunity Attachment to SAP Business Suite
Note: A Quotation was created in SAP ERP as a follow up document from the Opportunity in C4C
Pricing in Opportunity Follow Up Scenario in SAP Business Suite
Outbound Services C4C:
-
- Request Opportunity Data from SAP Business Suite
Sales Order Replication from SAP Business Suite
Inbound Services C4C:
-
- Replicate Sales Order from SAP Business Suite
-
- Replicate Sales Order Attachment from SAP Business Suite
Outbound Services C4C:
-
- Confirm Customer Order Replication to SAP Business Suite
Additional Configuration:
-
- Sales Order Extension
A custom field was added to the sales order in C4C and SAP ERP including integration. The procedure of the extension scenario is described in the blog post C4C blog post “Cloud for Customer Integration with ERP – create and replicate an enhancement field in sales order”
(https://blogs.sap.com/2018/04/24/cloud-for-customer-integration-with-erp-create-and-replicate-an-enhancement-field-in-sales-order/)
- Sales Order Extension
Sales Order Replication to SAP Business Suite
Outbound Services C4C:
-
- Replicate Sales Order to SAP Business Suite
-
- Replicate Sales Order Attachment to SAP Business Suite
Additional Configuration:
-
- Sales Order Extension
A custom field was added to the sales order in C4C and SAP ERP including integration. The procedure of the extension scenario is described in the blog post C4C blog post “Cloud for Customer Integration with ERP – create and replicate an enhancement field in sales order”
(https://blogs.sap.com/2018/04/24/cloud-for-customer-integration-with-erp-create-and-replicate-an-enhancement-field-in-sales-order/)
- Sales Order Extension
Pricing in Sales Order Replication Scenario in SAP Business Suite
Synchronous outbound Services C4C:
-
- Request Sales Document Data from SAP Business Suite
Business Document Flow Query from SAP Business Suite
Synchronous outbound Services C4C:
-
- Request Document Flow from SAP Business Suite
Print Preview of Business Documents in SAP Business Suite
Synchronous outbound Services C4C:
-
- Request Business Document Print Preview from SAP Business Suite
Landscape
The conversion project was performed on the following system landscape, all systems had the current version during time of testing.
-
- SAP Cloud for Customer Release 1802
-
- SAP Cloud Platform Integration
-
- Integration Packages:
-
- SAP Hybris Cloud for Customer Integration with SAP ERP – Version 1711
-
- SAP Hybris Cloud for Customer Integration with SAP S/4HANA – Version 1802
-
- SAP Cloud Platform Cloud Connector
-
- SAP ERP on HANA
-
- SAP S/4HANA On Premise

Figure 3: 01_03 System Landscape
.Setup and Conversion Phases
This chapter describes the detailed steps we carried out during the setup and conversion phase of our project. The procedure primarily describes the approach within a test landscape. However, the necessary steps in a productive landscape vary in some cases (for example: Integration artifacts are changed and tested in the test landscape and later imported to prod).

Figure 4: 02_02 Process Overview
The activities of the different phases are mainly driven by the conversion activities relevant on the SAP ERP and resulting S/4HANA system. With the technical conversion from SAP ERP to S/4HANA the SAP ERP customers and vendors will be converted to and synchronized with the business partner model. This is managed through the Customer Vendor Integration Module (CVI). With the actual conversion to S/4HANA the synchronization direction changes from the Business Partner (as the leading model) to Customer/Vendor.

Figure 5: 02_01 CVI Synchronization Direction
The additional business partner model in S/4HANA has impact on the integration with SAP Cloud for Customer. Hence with S/4HANA the integration scenarios need to change from Business Partner Replication from/to SAP ERP to Business Partner Replication from/to SAP Business Suite.
Phase 0: Setup & Initial Test
This phase was relevant in our conversion project as we had to setup the integration in our landscape from scratch. However, we recommend customers to run the conversion test in a full copy of the productive landscape (including the full set of data). Hence the setup and test of the integration scenarios might also be an initial step in a customer project. Initial test actually means to test all relevant scenarios with selected data to document the integration is running properly before the conversion activities start.

Figure 6: 02_08 Test and Prod Landscape
Relevance for customers:
-
- We recommend running the complete conversion beforehand in a test environment which is a full copy of the productive environment including all master and transactional data.
-
- The basis of the initial test is a catalogue of test cases for all integration scenarios. With the initial test the properly running scenarios (including the test data used) are confirmed beforehand. The test scenario catalogue can be used for the final test after the technical conversion activities.
This step is optional but strongly recommendedWe recommend testing all integration scenarios end to end:
Examples:-
- Run the replication including their confirmations
-
- Make sure synchronous integration scenarios are included (document flow; print preview in document flow; external price request; attachment replication; customer fact sheet)
-
- Make sure filter and/or system determination configurations/logic is tested (prospect blocking; filter BAdIs in SAP ERP or C4C; segment filter in SAP ERP)
-
- Make sure customer specific extension of the replication scenarios are tested
-
- The basis of the initial test is a catalogue of test cases for all integration scenarios. With the initial test the properly running scenarios (including the test data used) are confirmed beforehand. The test scenario catalogue can be used for the final test after the technical conversion activities.
Phase 1: Preparation Phase
This phase primarily covers activities on the SAP ERP side to implement the CVI module and to run the necessary CVI steps to prepare synchronization of customer/vendor data with the business partner. The activities were performed in our project by CVI experts together with the administrators of the SAP ERP system.

Figure 7: 02_03 Phase 1: Preparation
During this phase the system integration is still up and running and the main activities are on SAP ERP side to configure the CVI module.
We recommend to not have any unprocessed messages in the queue during the conversions. Any customers with a larger number of unprocessed message in the message queues are recommended to start in this phase the cleanup of unprocessed messages in test and in prod.
Relevance for customers:
-
- Relevant for test and productive landscape
-
- Plan and prepare the SAP ERP preparation activities along the recommendations, guides and cookbooks available for that topic with conversion experts involved.
-
- Check the number of unprocessed message at least in the productive environment and start as early as possible with the message clarification especially in case of large message numbers (e.g. messages with errors)
-
- Document the effort, durations and issues encountered during the test in the test environment. This helps to plan and schedule the final activities on production.
Phase 2: Synchronization
In this phase mainly, the synchronization of the customers to business partners through CVI is performed in SAP ERP according to the recommendations of the guidelines and conversion experts. Basically, a downtime of the SAP ERP system is recommended by SAP. This is a topic which needs to be clarified in detail with the conversion experts including the clarification of the impact of that downtime on the integration with C4C. Basically C4C can be operative during this phase but outbound messages from C4C will remain unprocessed in the message queue and synchronous messages calls (for example external price request) will throw an error message in case the SAP ERP system has a downtime. Unprocessed asynchronous C4C outbound messages need to be restarted in C4C Web Service Message Monitor once the SAP ERP system is back.

Figure 8: 02_04 Phase2: Synchronization
Relevance for customers:
-
- Relevant for test and productive landscape
-
- Plan and prepare the SAP ERP synchronization activities along the recommendations, guides and cookbooks available for that topic with conversion experts involved.
-
- Clarify downtime relevance of SAP ERP and impact on integration
-
- Re-start unprocessed asynchronous outbound messages in C4C in case C4C was up during SAP ERP downtime
-
- Document the activities and efforts to plan and schedule the final activities on production.
Phase 3: Conversion to S/4HANA
In this step the technical conversion from SAP ERP to S/4HANA will be performed. The conversion requires a technical downtime of SAP ERP. Since after that steps the SAP ERP APIs are no longer working, C4C also needs to be disconnected for user access and technical connectivity to prevent data inconsistencies.
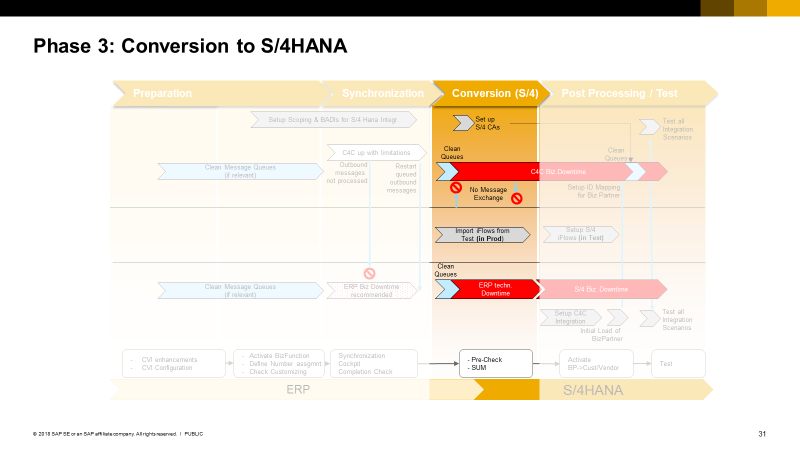
Figure 9: 02_05 Phase 3: Conversion
Before the systems are disconnected all unprocessed messages in the message queue need to be finally resolved. Disconnecting the systems and starting the downtime requires a dedicated proceeding especially when replication events can be triggered by background jobs or workflows:
-
- Start the process after all unprocessed messages in the message queue are resolved
-
- Lock all business users in C4C and SAP ERP to prevent any user activities which can cause replication messages in parallel to the technical downtime in SAP ERP.After all business users had been locked in C4C, outbound messages can still be created through the connectivity with other systems, background jobs or workflows in C4C. For all customers where this is relevant we propose the following steps:
-
- Activate scoping for the S/4HANA relevant integration scenarios. This step can also be done during the preparation phase:
Scoping: Communication and Information Exchange à Integration with External Applications and Solutions à Integration of Master Data
à Do you want to replicate business partners from an external application to your cloud solution?
à Do you want to replicate business partners from your cloud solution to an external application?
à Do you want to block prospects created in your cloud solution from being replicated to an external application?
- Activate scoping for the S/4HANA relevant integration scenarios. This step can also be done during the preparation phase:
-
- Implement existing customer specific filter BAdI logic for the SAP ERP messages also for the S/4HANA messages if relevant. This step can also be done during the preparation phase:
à Assign 1297 – Request Business Partner Replication, 1298 – Request Business Partner Relationship Replication, 1366-Request Business Partner Direct Responsibility Replication in the PDI enhancement option: “CheckBusinessObjectInstanceProcessIntegrationRelevance”
- Implement existing customer specific filter BAdI logic for the SAP ERP messages also for the S/4HANA messages if relevant. This step can also be done during the preparation phase:
-
- Deactivate workflows to inactive if relevant
-
- De-schedule MDROs (PDI developed MDROs) if relevant
-
- Change credentials or remove client certificate from technical users used for any 3rd party system inbound communication.With these steps any system-based activity causing replication relevant changes, should be deactivated. In case there are any hidden processes which could still trigger replication relevant changes, the setup of the S/4HANA communication arrangements could catchup those changes for re-processing once the systems are re-connected after conversion:
-
- Setup the relevant communication scenarios for the S/4HANA Business Partner Replication. The communication system remains the existing SAP ERP system.
-
- Change the service endpoints in all C4C outbound communication services from the CPI IFlow endpoints relevant for SAP ERP integration to the S/4HANA relevant CPI IFlow endpoints.These communication arrangements are used to generate replication messages coming in from any background process or 3rd party integration, which had not been deactivated before. As at this stage the ID mapping btw. C4C and S/4HANA has not yet been setup, any business partner relevant messages cannot be reprocessed when both systems are reconnected again. However, the business partner related messages still can be used to log any changes on customers and to re-reprocess those changes at least manually if relevant. Messages created for transactional documents can be processed when the systems are re-connected
-
- Lock all business users in C4C and SAP ERP to prevent any user activities which can cause replication messages in parallel to the technical downtime in SAP ERP.After all business users had been locked in C4C, outbound messages can still be created through the connectivity with other systems, background jobs or workflows in C4C. For all customers where this is relevant we propose the following steps:
-
- Final check on any unprocessed SAP ERP relevant messages
-
- Start SAP ERP technical downtime according to the recommendations of the guidelines and conversion experts.
Relevance for customers:
-
- Relevant for test and productive landscape – C4C and SAP ERP are down
-
- Plan and prepare the SAP ERP conversion activities along the recommendations, guides and cookbooks available for that topic with conversion experts involved.
-
- Final resolving of unprocessed messages in C4C and SAP ERP before you start the downtime
-
- The downtime planning of the productive system need to be derived from the downtime encountered during the test landscape conversion.
-
- In production the S/4HANA relevant iFlows adjusted and tested during the test setup can be imported to the middleware.
Phase 4: Post Processing
The post processing starts after the technical conversion of the on-premise system to S/4HANA. In this step the connectivity on the new S/4HANA endpoints will be setup and the Business Partner ID Mapping is retrieved from S/4HANA. During these activities the systems are down for business users.

Figure 10: 02_06 Phase4: Post Processing
We used the SAP Best Practice Guide “SAP Best Practices for SAP S/4HANA integration with SAP Hybris Cloud for Customer” to get guided through the detailed set up steps in S/4HANA. (https://support.sap.com/content/dam/SAAP/Sol_Pack/RDS_CFC_S4_INT/RDS_CFC_S4_INT_CFCALL_09_Content_Li…) 1EL – Basic Integration setup using Cloud Platform Integration
Although the integration setup in the converted system is slightly different, the best practice guides are a good reference document.
Here are the steps we performed while the systems were down for business:
-
- The connectivity btw. C4C and the S/4HANA system had to be established. During the previous conversion steps in C4C we already set up and adjusted the communication arrangements for the S/4HANA integration and implemented the filter and system determination BAdIs of the new business partner integration scenarios.
-
- In the middleware, in our case CPI, we had to setup and deploy the iFlows for the S/4HANA replication scenarios. We also adjusted and extended the iFlows with customer specific settings. At this stage it pays off if you have documented all iFlow adjustments in detail during the initial implementation.
In a customer environment this step is only relevant in the test landscape. In the production landscape the iFlow adjustment can be done by importing the tested iFlows from the test environment.
- In the middleware, in our case CPI, we had to setup and deploy the iFlows for the S/4HANA replication scenarios. We also adjusted and extended the iFlows with customer specific settings. At this stage it pays off if you have documented all iFlow adjustments in detail during the initial implementation.
-
- In S/4HANA the integration with C4C had to be setup. We followed the best practice guide for those steps which were relevant after the conversion. The re-setup also requires running the RCOD_CONNECTIVITY report. Once done, we double checked the endpoints to match with those in the iFlows.
In the SAP ERP system, we have implemented segment and BAdI filter for the Business Partner replication. Those filters had to be re-implemented in the S/4HANA Data Replication Framework (Transaction: DRFF). In our case we had segment filters for filtering out a specific sales area from being replicated within the business partner replication.
- In S/4HANA the integration with C4C had to be setup. We followed the best practice guide for those steps which were relevant after the conversion. The re-setup also requires running the RCOD_CONNECTIVITY report. Once done, we double checked the endpoints to match with those in the iFlows.

Figure 11: 02_07_DRFF_Filtersettings
-
- In our first test the segment filter was ignored. Hence, we had to uncheck the system filter in the DRFIMG for the relevant Business Object.DRFIMG –> Define Custom Settings for Data Replication –> Define Technical Settings –> Define Technical Settings for Business Systems –> Select Biz System (0LOAVOJ) –> Define BusSystems, BOs -> Uncheck SysFilt. for BO Type 986In addition, filter criteria for the replication relevant for Business Partner roles had to be implemented.
-
- Start the initial load of the business partners from S/4HANA –> Transaction: DRFOUT (or COD_INT_MENU –> Initial Load or Resend Objects from S/4HANA to SAP Cloud for Customer)After the conversion the business partner is the leading model which is automatically synchronized with the customer through the CVI module. Thus, the business partner replication btw. S/4HANA and C4C also need to be setup according to this model change.In C4C the following IDs are mapped in the ID mapping:
a. Employee ID
b. SAP ERP customer ID
c. Customer Contact Relationship IDThe new model requires to set up a business partner ID mapping in parallel.
The initial load of the business partner is required to setup that business partner ID mapping in C4C.
Done Correct the initial load will not duplicate the business partner records as the replication message also contains the existing ID. As C4C logic recognizes the existing ID in the mapping table, it just creates a new ID mapping entry for the Business Partner ID Mapping. In the current scope the ID mapping setup requires the business partner initial load.
We recommend running the initial load of the business partner with the full set of productive data in test to track the replication time. The productive downtime can then be scheduled and planned based on that information.To prevent duplicate business partner entries, initial load of business partner must be performed and restricted in the order specified below, ensuring that business partners are not replicated before the corresponding ID mapping is created.
Restriction is done by setting “Manual Replication Filter Criteria” in transaction DRFOUT.
To enable a filter field (right side), double click the field name on selection list (left side).
a) Initial load of Employees without relationships.(only if applicable) to create Employee ID mappings in Cloud for Customer1. To exclude Relationships, add the Field Selection BPSelectionMode (double click)
2. Select BPSelectionMode “1 – Business Partners Only”
3. Only BusinessPartners with BP Identifier Identification Type “HCM001”
(Business Partners with an Employee ID)
b) Initial load of Customer Business partners without Partner Functions and without Relationships to create Business Partner IDsImportant Node:
Since the Partner Functions need to be excluded, the iflow needs to be modified to prevent deletion of the partner functions missing in the message in SAP Cloud for Customer.
To do so, in CPI the “Replicate Business Partners from SAP Business Suite” iflow needs to be copied and in S4 the destination URL of the copied iflow needs to be set as destination.
In the iflow on the BusinessPartner->Customer->SalesArrangement element the PartnerFunctionLIstCompleteTransmissionIndicator attribute must be set to “false”
After initial load the URL in S4 should be reverted to the original unmodified iflow.1.Exclude Relationships using BPSelectionMode “1 – Business Partners Only”
2.Open Multiple Selection Screen for Partner Functions
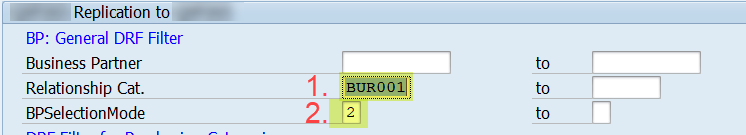
3.Exclude Range “00” to “ZZ” c) Initial load of Contact Relationships
c) Initial load of Contact Relationships
1. Select Contact Relationships, category “BUR001”
2. Use BPSelectionMode “2 – Relationships Only”
- Start the initial load of the business partners from S/4HANA –> Transaction: DRFOUT (or COD_INT_MENU –> Initial Load or Resend Objects from S/4HANA to SAP Cloud for Customer)After the conversion the business partner is the leading model which is automatically synchronized with the customer through the CVI module. Thus, the business partner replication btw. S/4HANA and C4C also need to be setup according to this model change.In C4C the following IDs are mapped in the ID mapping:
-
- Clean up the queues on either side in case any messages had been triggered during the downtime.
-
- Test each integration scenario before activating the user to make sure the integration with S/4HANA is running properly. During those tests we have encountered some issues which required adjustments. The list below shows the issues we identified. Please note, this list is not representative due to individual scenario and system setup, but it might give you a guidance in case you step into related topics:
-
- Dump in S4 quote when opening output: RCOD_OUTPUT_COD1 is not in the library. Corrected by removing COD1 from Output procedure V06000
-
- iFlow: Confirm Contract Replication to SAP Business Suite. Processing of inbound IDOC fails in S/4. Had to apply note 2570752.
-
- iFlow: Confirm Customer Order Replication to SAP Business Suite. Inbound confirmation message failed “No parameters found for function module &”
had to apply SAP Note 2632743
- iFlow: Confirm Customer Order Replication to SAP Business Suite. Inbound confirmation message failed “No parameters found for function module &”
-
- S/4 Sales Order Processing. “IDoc cannot be sent to an XML port EDI: Syntax error in IdocSales Order Processing”
-
- Had to change Basic IDoc Type from COD_REPLICATE_SALES_ORDER01 to COD_REPLICATE_SALES_ORDER02 in transaction WE20 manually, connectivity report did not update
-
- In S/4HANA it is possible to maintain non-sales area related relationships in addition to the sales area related partner functions which are also relevant in SAP ERP. Creating a business partner relationship on employees requires to adjust the segment filter in S/4HANA to allow the replication of Employees (BUP003) and to adjust code list mapping “Party Role Code” to map Employee Responsible to Type Code BUR011.
This scenario requires the employee being replicated as business partner. During our conversion project the employee replication model was not finally settled. In case customers decide to extend the business partner in S/4HANA with the relationships using employees, the employee replication model need to be clarified with the S/4HANA experts and C4C expert service. Since this is not a scenario directly related to the conversion (SAP ERP uses sales area depended party functions) this topic is rather to be considered as a functional extension scenario after conversion.
- In S/4HANA it is possible to maintain non-sales area related relationships in addition to the sales area related partner functions which are also relevant in SAP ERP. Creating a business partner relationship on employees requires to adjust the segment filter in S/4HANA to allow the replication of Employees (BUP003) and to adjust code list mapping “Party Role Code” to map Employee Responsible to Type Code BUR011.
-
- Test each integration scenario before activating the user to make sure the integration with S/4HANA is running properly. During those tests we have encountered some issues which required adjustments. The list below shows the issues we identified. Please note, this list is not representative due to individual scenario and system setup, but it might give you a guidance in case you step into related topics:
-
- Reactivate the workflows and MDROs if relevant
-
- Re-set changed credentials or re-assign client certificate to technical users used for any 3rd party system inbound communication
-
- Activate the business users in C4C in parallel to opening up S/4HANA.
-
- Document all steps including the duration and corrections during the test to plan your conversion for the productive tenant upon this information.
After the conversion, ID mapping is maintained in C4C for both the customer and the business partner. Hence the external ID shown in the Account TI might not be unique anymore (depending on the numbering model set up in the CVI conversion). To see both ID mappings in the account, the facet “Mapping for Integration” can be added which shows all ID mappings listed

Figure 12: 02_09 Mapping for Integration
We also had an SAP ERP cockpit mashup integrated in the sales data of the account to achieve a 360° view on the SAP ERP data in C4C. As the SAP ERP cockpit is no longer available in S/4HANA this approach need to be substituted by other approaches. The C4C blog post “Cloud for Customer Mashup: Call an ERP transaction in SAP GUI for html” provides information on alternate approaches (https://blogs.sap.com/2018/02/15/cloud-for-customer-mashup-call-an-erp-transaction-in-sap-gui-for-ht…)
With 1808 a standard mashup is available in C4C for the account 360° view with S/4 HANA.
During our validation project the final handling of employee data with PERNR and Business Partner ID in an integration environment was not settled. It also depends on the actual landscape. C4C matches the incoming BusinessPartner message with the existing employee based on the PERNR. In a customer project the replication approach need to be clarified upfront with expert involvement.
Relevance for customers:
-
- Relevant for test and productive landscape – C4C and SAP ERP are down
-
- Plan and prepare the SAP S/4HANA post processing activities along the recommendations, guides and cookbooks available for that topic with conversion experts involved.
-
- The downtime planning of the productive system need to be derived from the downtime encountered during the test landscape post processing activities.
-
- To setup the ID mapping for business partner an initial business partner load is required.
-
- In test the S/4HANA relevant iFlows are implemented and adjusted. Intensive tests need to be carried out to validate the correctness of the integration setup.
-
- Re-start any unprocessed messages in C4C and SAP S/4HANA if any occurred before you activate user access to the systems.
Alternative variant including pro/con assessment
The procedure described in the above section is very restrictive regarding the availability of the C4C system for the business users, to ensure that the data remains in sync in C4C and S/4HANA.
Basically, the C4C system has a business downtime during the complete Conversion and Post Processing phases, parallel to the S/4HANA technical and business downtime. In most cases the conversion to S/4HANA can be performed on a weekend, during which a business downtime of C4C is acceptable. However, in some cases (for example when a large set of business partner data are affected) the conversion to S/4HANA can take longer than a weekend. In such cases it might be required that C4C is available for business users during the phases Conversion and Post Processing.
In this section an alternative variant is described to reduces the business downtime of C4C to a necessary minimum. This might be relevant only for the conversion of the production system.

Figure 13: 03_01 Reduces Downtime Approach
However, as the downtime of S/4HANA remains the same, C4C will enable a limited functionality during this period. Limitations are relevant for the functions that require an integration to SAP ERP or S/4HANA. All SAP ERP integration-based features, such as External Pricing, will not be available as well. If a bidirectional replication is configured, some objects, such as Contract and Sales Order, are set to read-only after a change in C4C until the confirmation message from SAP ERP is processed. The objects will remain in read-only mode until C4C receives a confirmation messages from the SAP ERP or S/4HANA.
Once the on-premise system is up and running again, the queued outbound messages in the C4C Web Service Message Monitor must be restarted and processed by S/4HANA. This also triggers the exchange of the confirmation message and by that to unlock the effected business documents. It is possible to unlock the relevant business objects also manually: TI facet “Transfer Logs” > gear wheel > “Revoke Transfer. This however, this should be avoided, as it interferes with the replication sequence.
Monitoring and Restarting Web Service Messages
While the target system (SAP ERP or S/4HANA) is not available, the outbound messages will run into connectivity errors. These errors are logged by erroneous replication messages in the Web Service Message Monitor (WoC Administrator > General Settings > Web Service Message Monitoring). Once the target system is available, the messages can be restarted. Further details on the Web Service Message Monitor can be found in the SAP Help Portal “Web Service Message Monitoring” (https://help.sap.com/viewer/5d3ae4aa1f174b2cb6ec625c93ef8884/1808/en-US/98c0b9ea6d8e1014a79e979addd0…).
Please note, the messages must be restarted in chronological order, from old to new, to ensure data consistency between the systems. Also consider the object dependencies and start first with master data like business partners and continue with related data like business partner relationship and transactional documents.
Do not restart all messages at once but start with one message and check if it properly arrives and can be processed in the target system. Then continue with a small number of messages and monitor the replication end-to-end. Increase the number of restarted messages as long as the messages are replicated and processed successfully. Consider that confirmation messages are sent by the target system, which can add additional load.
Synchronous messages, like External Pricing, do not need to be restarted. They can be cancelled in the Web Service Message Monitor and triggered again from within the respective transactional object.
Deviation from the standard procedure
Preparation Phase
-
- No deviation
Synchronization Phase
It is recommended to have a business downtime of SAP ERP during the CVI Conversion. During the SAP ERP downtime of the synchronization phase a parallel C4C downtime is technical not required.
In case C4C is up and running during this phase, functional limitations in C4C need to be considered – all SAP ERP integration-based features, such as External Pricing, will not be available.
Any outbound message in C4C, will then run into an error, as SAP ERP is not available. The failed outbound messages are queued in the Web Service Message Monitor (WoC Administrator > WCF General Settings).
-
- After the downtime of SAP ERP, clean up the queue in chronological order as described above.
Conversion Phase
In the conversion phase the SAP ERP system is converted into a S/4HANA system. During the conversion, the system is down and cannot receive or send any messages. In this phase it is possible to reduce the C4C business downtime to an absolutely necessary minimum.
In case C4C is up and running during the business downtime of S/4HANA, C4C operates with functional limitations. All integration-based features, such as External Pricing will not be available.
Any outbound message in C4C relevant for S/4HANA will run into an error. The failed outbound messages are listed in the Web Service Message Monitor (WoC Administrator > WCF General Settings).
-
- At the beginning of the Conversion phase, lock all business users in C4C (business downtime), as well as in SAP ERP.
-
- In case you expect replication relevant changes of data performed by workflows, MDROs and integrated systems during the C4C business downtime, deactivate the respective workflows, de-schedule MDROs (PDI developed MDROs) and deactivate the inbound integration.
-
- Scope and set up the S/4HANA integration in C4C.
-
- Activate scoping for the S/4HANA relevant integration scenarios and for blocking prospects for the S/4HANA replication if relevant. (this step can also be done during the preparation phase)
-
- Setup the relevant communication scenarios for the S/4HANA Business Partner Replication. Note: The communication system remains the existing SAP ERP system.
-
- Change the service endpoints in all S/4HANA relevant C4C outbound communication services from the previous SAP ERP to the S/4HANA specific CPI iFlow endpoints.
-
- Deploy the PDI Solution with filter BAdI logic for S/4HANA messages if relevant (this step can also be done during the preparation phase).
-
- Scope and set up the S/4HANA integration in C4C.
-
- Now the users can be unlocked to access C4C again. The deactivated workflows, MDROs and inbound integration can be re-activated as well. As described, all replication messages will run into connectivity errors, which need to be cleaned up and restarted at a later point in time to establish data consistency between the systems.
-
- Import the adjusted CPI IFlows for the S/4HANA integration into productive CPI tenant. Do not deploy the IFlows yet, to avoid that any messages reach the S/4HANA system before it is ready.
Post Processing Phase
At the end of the post processing phase, when S/4HANA is ready and the integration to C4C is set up, another business downtime of C4C is required to deploy the CPI IFlows in the production tenant and clean up / restart the erroneous messages in the Web Service Message Monitor. This activity might be performed outside the business hours, overnight or weekend, to reduce the impact on the business users.
-
- Lock all business users in C4C (business downtime), and deactivate workflows, de-schedule MDROs (PDI developed MDROs) and deactivate the inbound integration, if required.
-
- Deploy the CPI IFlows specific to the S/4HANA integration in the production CPI tenant.
-
- Clean up the erroneous messages in the Web Service Message Monitor
-
-
-
- The web service messages for Business Partner replication to S/4HANA (Replicate Business Partner […] to SAP Business Suite) were created while the S/4HANA Business Partner IDs were not known to the C4C ID Mapping for Integration. Hence, the Business Partner replication messages do not contain the Business Partner IDs which are required by S/4HANA. Therefore, these messages in the monitor must not be restarted, but used to identify the records that need to be replicated. To identify the business partners that need to be replicated, open the payload of each message and note the InternalID of the Business Partners.
-
- Once all relevant Business Partner IDs are noted, cancel the messages for Business Partners replication.
-
- Navigate to the work center Administrator > Extract Data to External System.
-
- Select “Replicate Business Partner” and provide the C4C (internal) Business Partner ID and the Business System ID of S/4HANA (same as the Business System ID of SAP ERP before the conversion).
-
- Execute the replication.
-
- Do not replicate all business partners at once but start with one record and check if it arrives properly and can be processed in S/4HANA. Then continue with a small number of records and monitor the replication end-to-end. Increase the number of records as long as the records are replicated and processed successfully. Consider that confirmation messages are sent back by S/4HANA, which can add additional load.
-
- Repeat the same steps for Business Partner Relationship messages, if applicable.
-
- Once the business partners are replicated from C4C to S/4HANA, restart the remaining messages in chronological order, to ensure data consistency across the systems.
-
- Synchronous messages, like External Pricing, do not need to be restarted. They can be cancelled in the Web Service Message Monitor and triggered again from within the respective transactional object.
-
-
-
- Now the users can be unlocked to access C4C again. The deactivated workflows, MDROs and inbound integration can also be activated again.
4. Summary
The conversion project must carefully be planned with experts involved (S/4HANA, CVI, C4C Integration). A business critical aspect is the required downtime of the relevant productive systems during the conversion activities. The execution of all activities based on the full set of productive data in a test environment is essentially recommended for the following reasons:
-
- Adjustments on integration artifacts (e.g. iFlows, BAdIs) need to be tested and imported from Test to Prod
-
- Conversion steps and durations need to be tested and logged during test and used to plan the productive conversion and downtime management
The project activities are primarily driven by the required steps of the SAP ERP to S/4HANA conversion. The preparation and planning of these activities also requires CVI and conversion expert knowledge.
The total conversion project time and the system downtimes depend on various factors:
-
- Know How
-
- Customer/Vendor/business partner set up complexity (e.g. number ranges)
-
- Data volume
-
- Customer specific enhancements/extensions
Please note: During our validation project the final handling of employee data with PERNR and Business Partner ID in an integration environment was not settled and also depends on the actual landscape. C4C matches the incoming BusinessPartner message with the existing employee based on the PERNR. In a customer project the replication approach need to be clarified upfront with expert involvement.
The major differences encountered during our conversion project are:
-
- Business Partner Model deviates from Customer/Vendor Model
-
- Numbering
-
- Replication Messages and message structure for BizPartner
-
- Business Partner Model deviates from Customer/Vendor Model
-
- The integration with the new Business Partner leads to two external IDs for accounts in Cloud for Customer which can be different
-
- Some UIs and reports show only one external ID
-
- In the Account/Contact UI a new facet can be added “Mapping for Integration” to see all external IDs
-
- The integration with the new Business Partner leads to two external IDs for accounts in Cloud for Customer which can be different
-
- SAP ERP cockpit no longer available in S/4HANA
-
- Need to be substituted by alternate S/HANA approaches (e.g. standard mashup available in C4C with 1808)
-
- SAP ERP cockpit no longer available in S/4HANA
-
- Different Integration Framework in S/4HANA
- S/4HANA has differences in the supported integration scenarios. Please check SAP note 2293815 – “S/4HANA Enterprise Management: Information about Integration Scenarios with SAP Cloud for Customer” with the list of supported scenarios.


